May 28, 2020 By BlueAlly

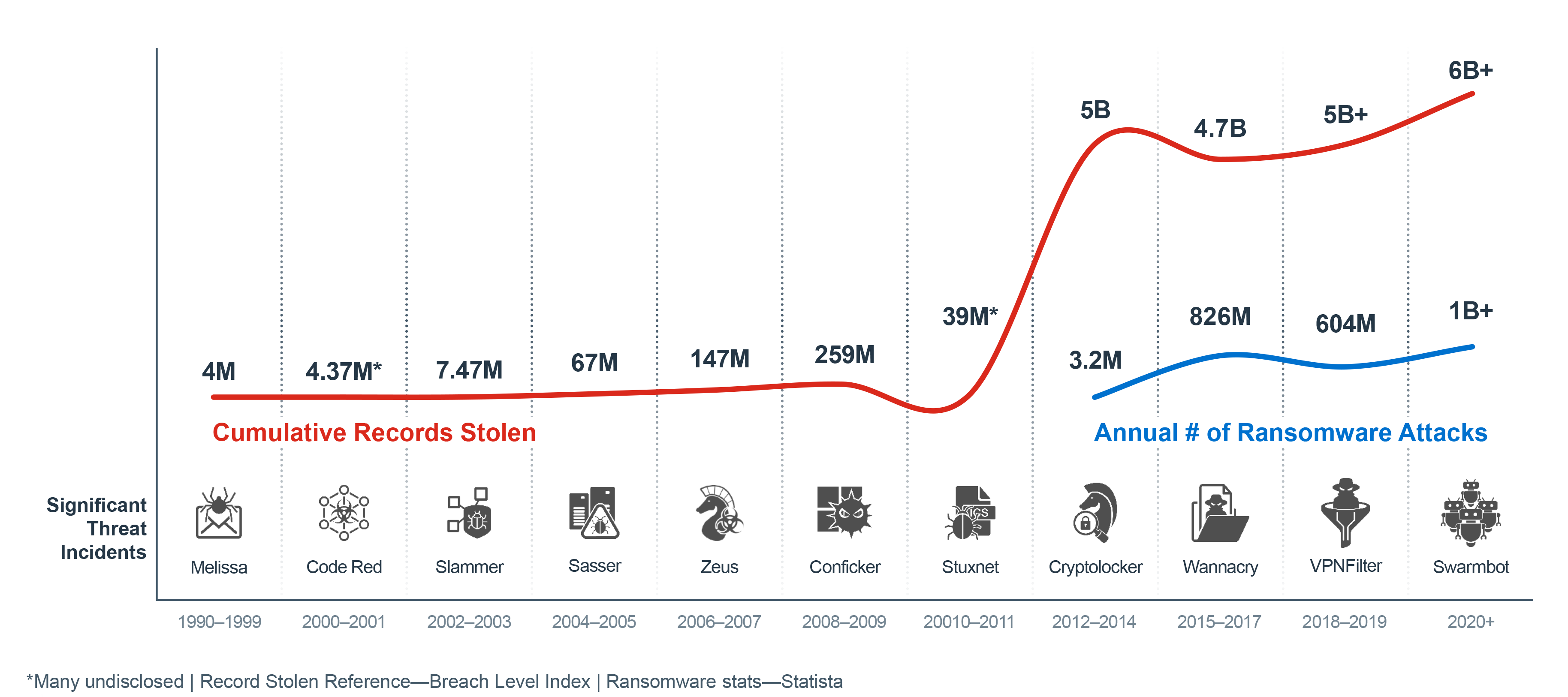
With 71% of ransomware attacks targeting small-to-medium sized businesses (SMBs), it continues to be the prevailing form of malware used by attackers to disrupt organizations. The rapid adoption of new digital innovations often introduces new security gaps and makes it easier for attacks to spread across the flat and open internal network. For many, the loss of critical business cycles and revenues from systems that have ground to a halt far outweighs the price of the ransom itself. The Fortinet Security Fabric provides comprehensive network security and advanced threat-intelligence sharing to help SMBs detect and protect against ransomware attacks.
Advanced Threats Continue to Adapt
Even advanced threats still rely heavily on social engineering

Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Important Communication.
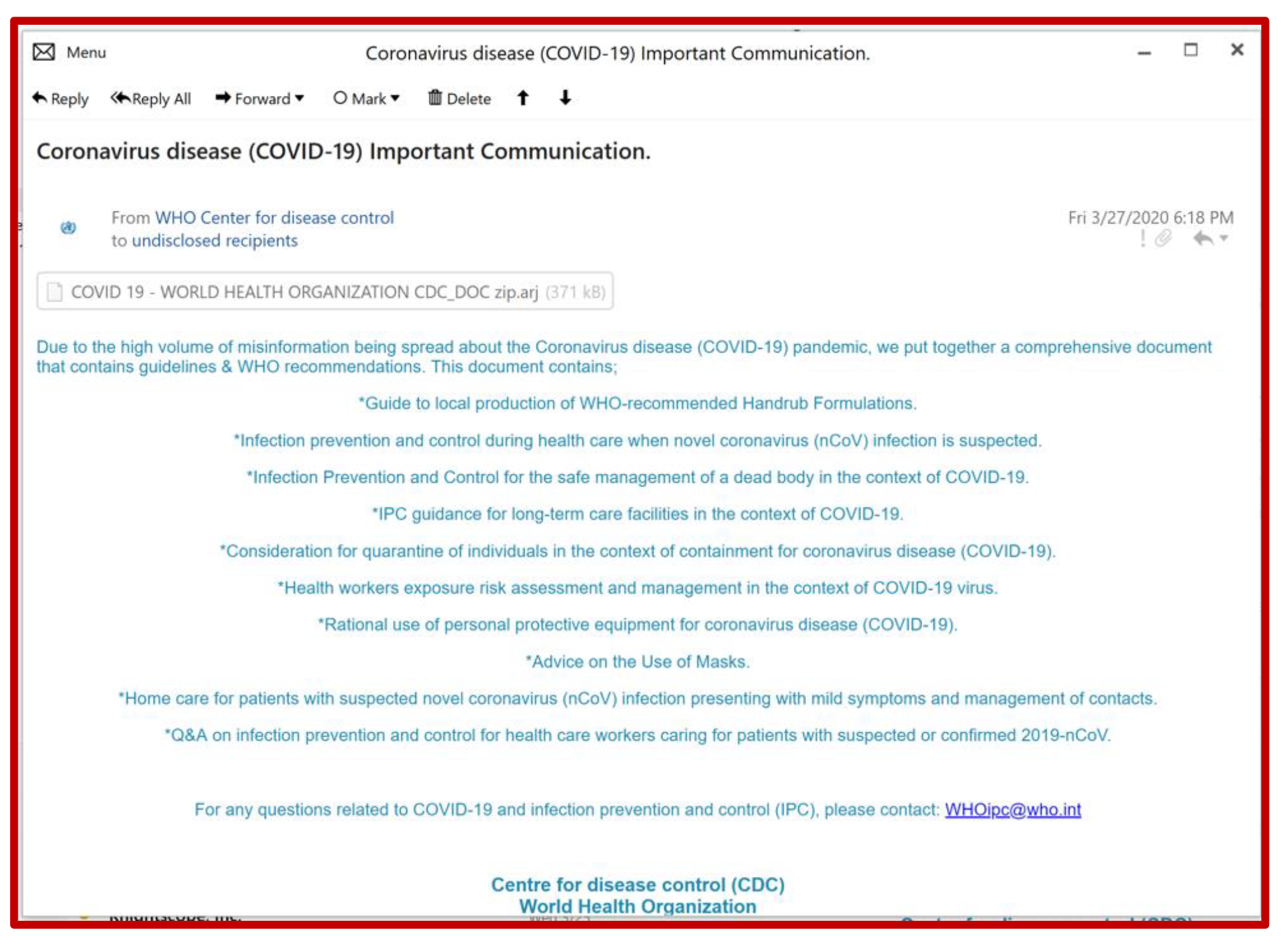
“Due to the high volume of misinformation being spread… we put together a comprehensive document that contains guidelines & WHO recommendations.”
CovidLock
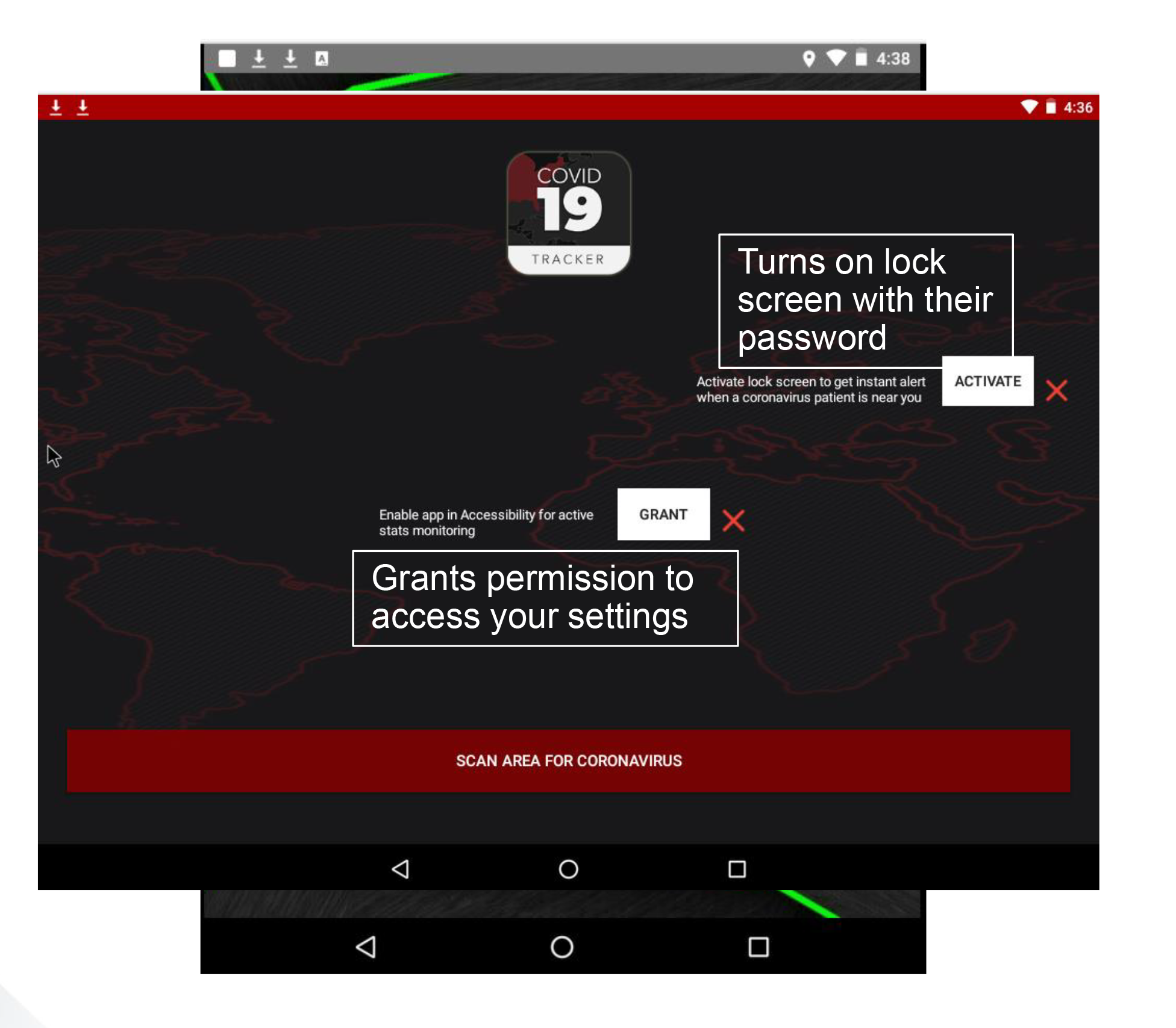
- Claimed real time outbreak tracking
- Screen lock attack
- Delivered on Android
SMB Ransomware Trends
How Ransomware Gets In
The pressing need for speed and agility across business’s of all sizes has led to the rapid adoption of innovations (e.g., cloud-based tools, Software-as-a-Service [Saas], smart devices) that bring convenience along with complexity—quickly creating vulnerabilities and making it easier for even basic threats to get past outdated defenses at various points of entry.
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) that enables attackers to merely invest in an attack carried out by others and the natural IT knowledge of younger generations have made it easier for low-level hackers to easily blast a wide target base and expose one of those holes and is one reason that has led to such high rates of SMBs being hit with ransomware.
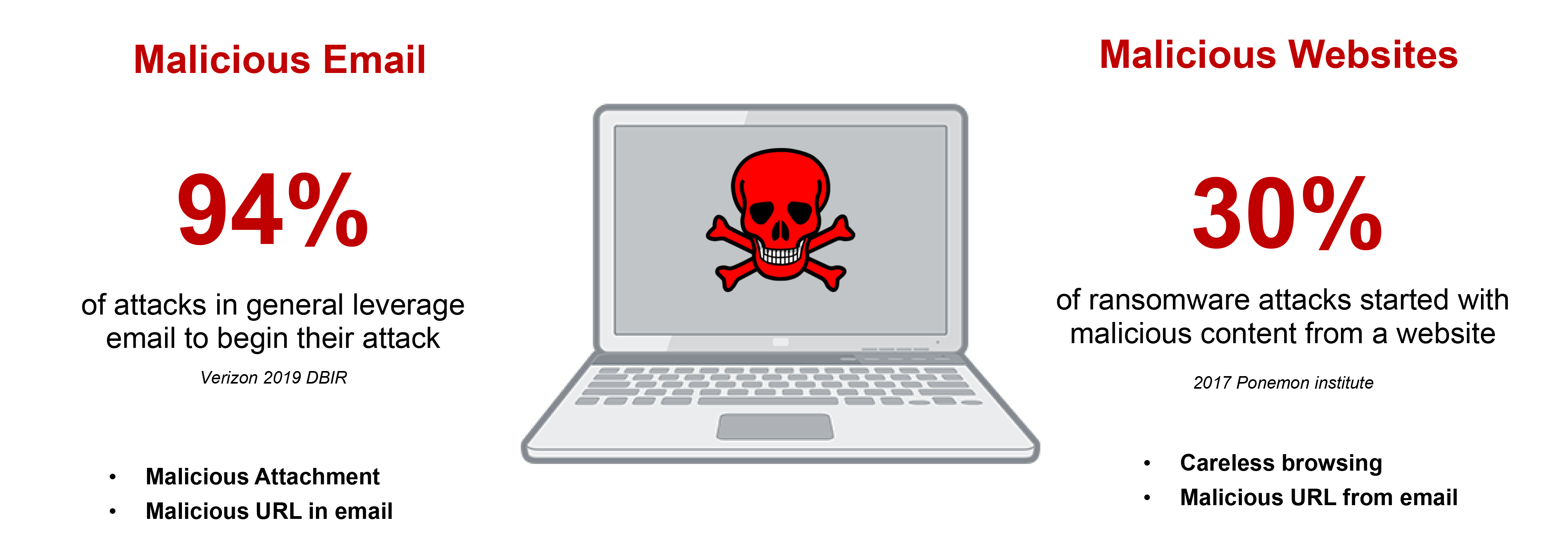
Email Vulnerabilities
Email is the primary way that ransomware gets inside a business’s network. Many users still unintentionally open a malicious attachment or URL that slips by consumer-grade email filters. More often these days, attackers rely on social engineering and business email compromise (BEC) scams where users unknowingly give attackers the information they seek to set off a series of events—like getting the victim’s phone number and replicating known sites to obtain user credentials. For SMBs that often rely on consumer-based email solutions that lack advanced email security checks, recognizing threats and avoiding social engineering schemes rely on a user’s individual judgment to identify the threat and avoid infection.
Was It Only Ransomware?
If ransomware was introduced into the network, then attackers gained access. While ransomware may have been the primary motive, other nefarious tools—such as monitoring software, command-and-control (C&C) code, or assimilation into botnets—may have also been introduced to launch additional attacks or siphon data at a later date. Therefore, any ransomware-compromised business must do further investigation into logs and systems for full and effective remediation.
How Does Ransomware Typically Work?
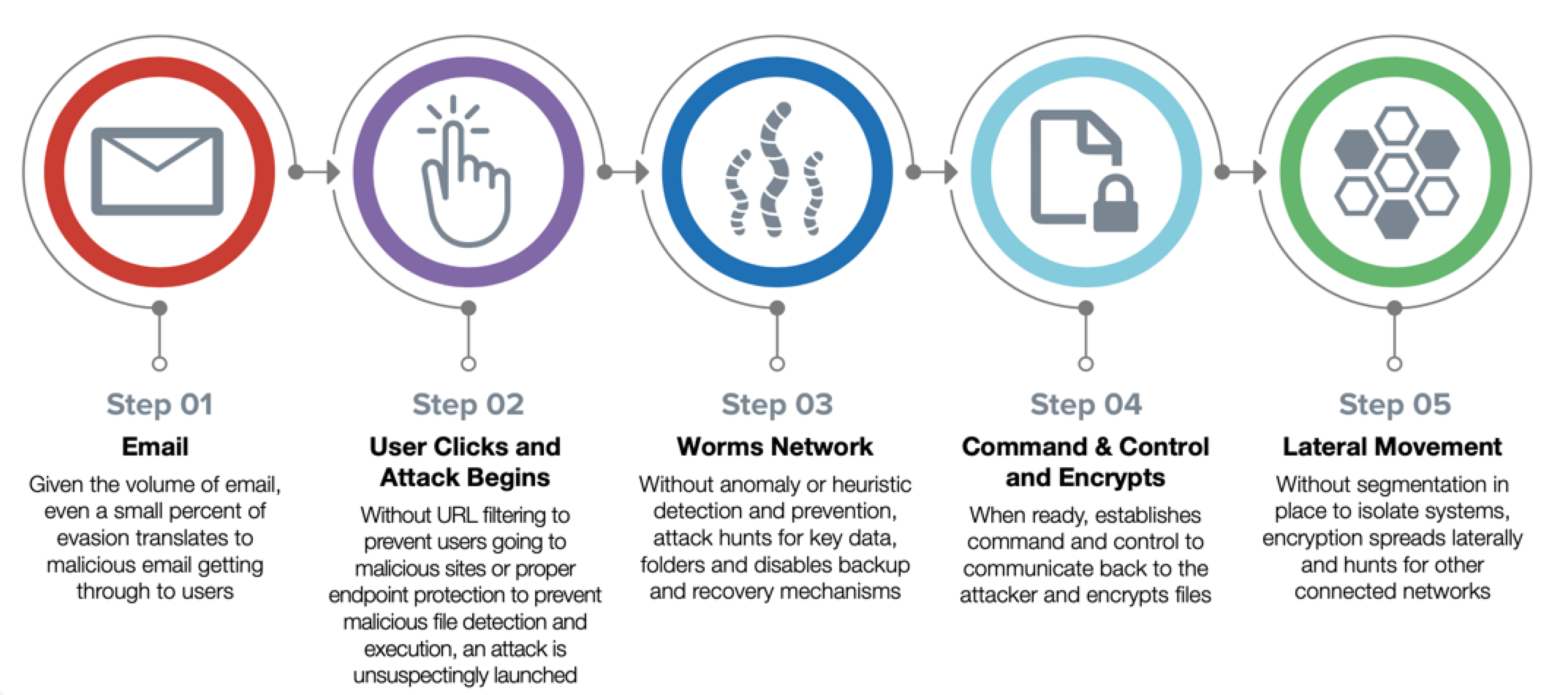
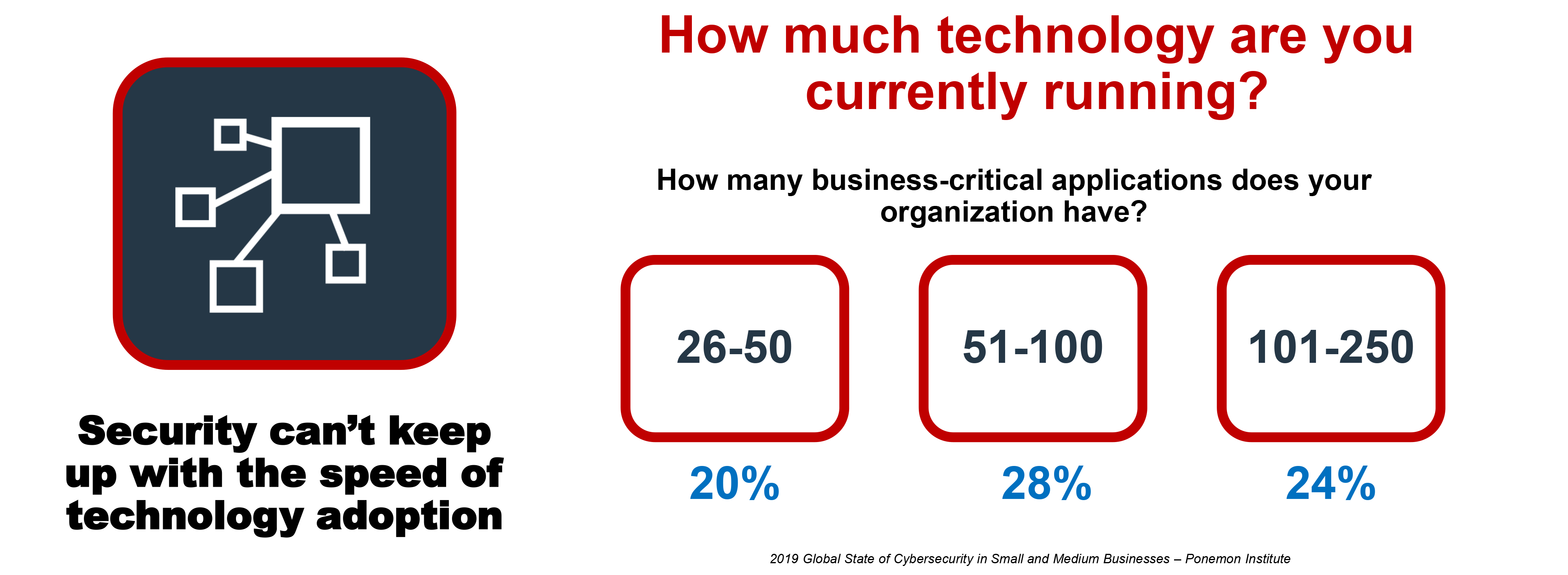
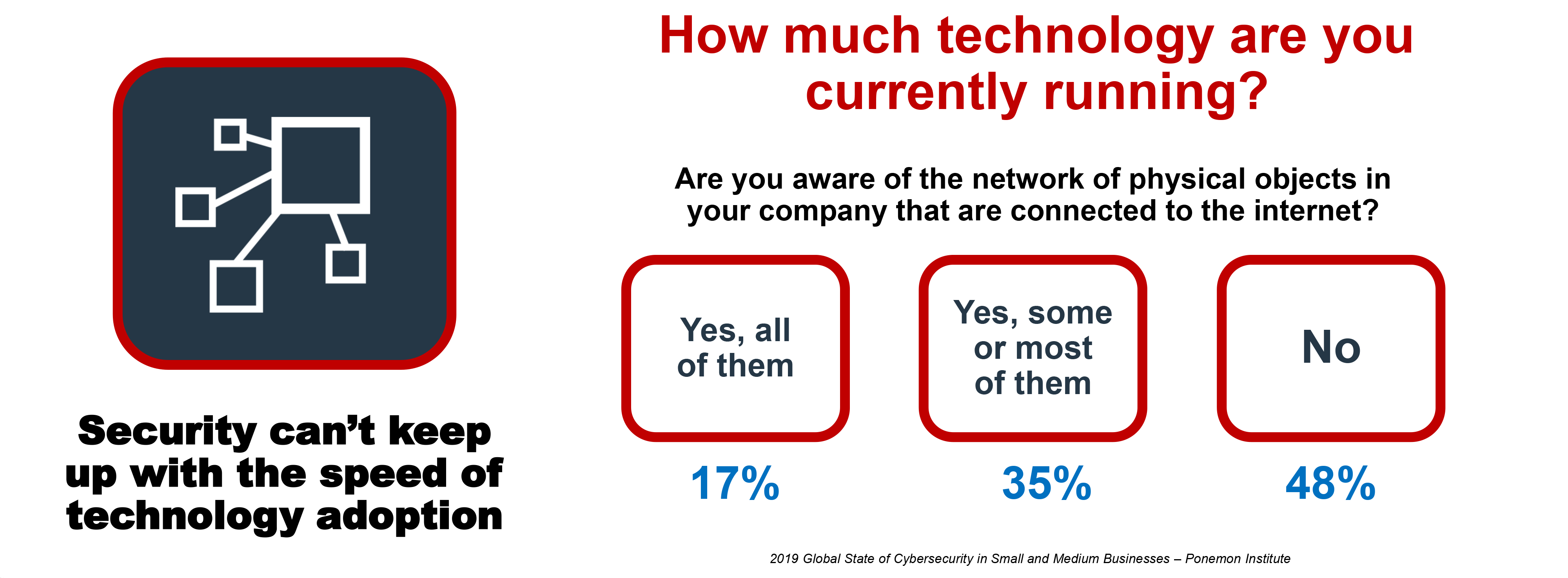
SMBs By the Numbers

Why the Numbers?

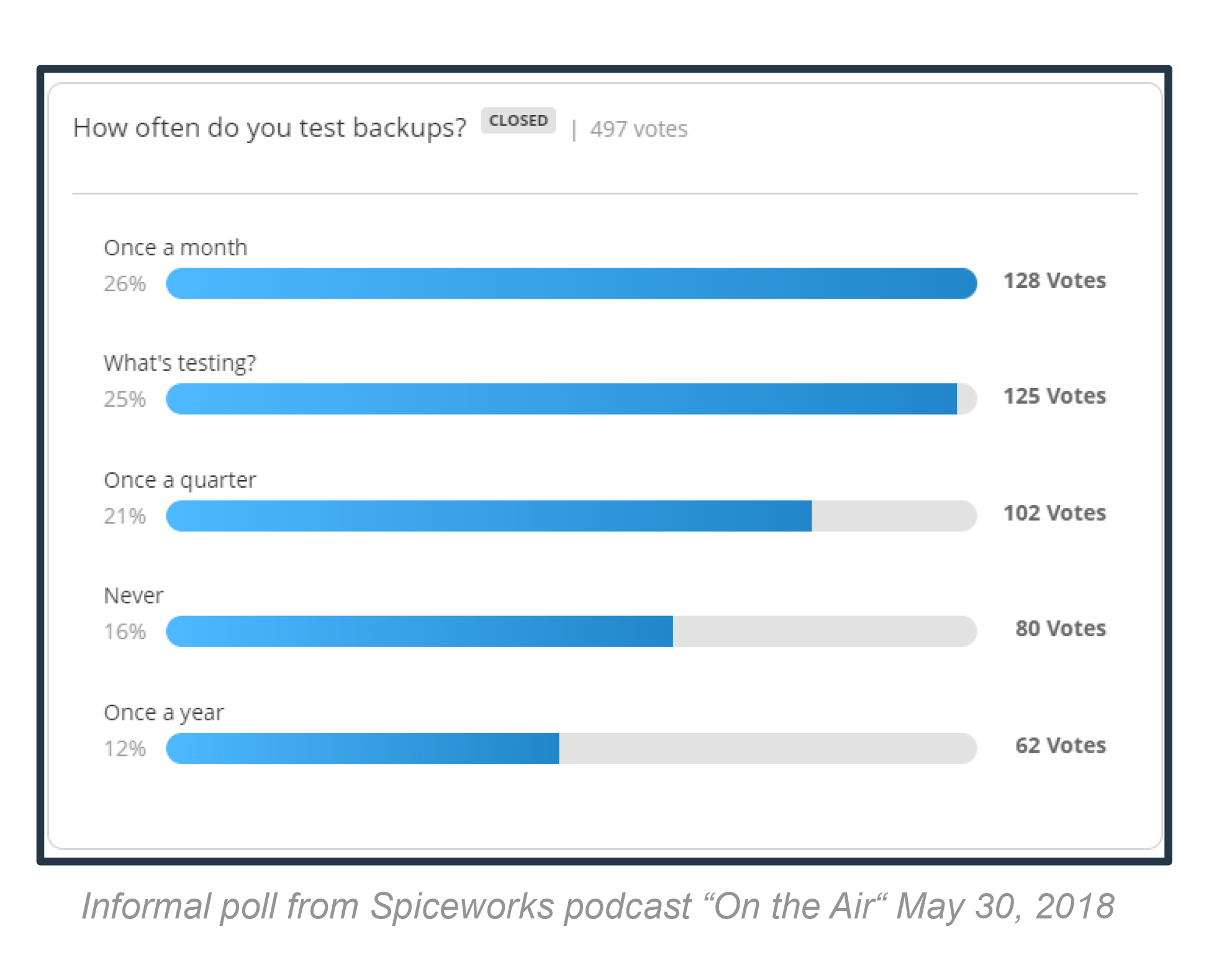
We Rely on Backup and Recovery
Single point of failure ok?
- When is the last time you tested your system?
- How long does it take to recover your databases?
- What happens if you get hit with something like SamSam or Ryuk that target backups?
A Successful Approach to SMB Security Must Be...

How Ransomware Avoids Traditional SMB Security
How Fortinet Can Help…
The Fortinet Security Fabric enables organizations to stop known and unknown ransomware across their environment through automated sharing of actionable intelligence.
Most Common Ways Ransomware Enters

How Malicious Emails Circumvent Security
Malicious Attachments

Inadequate analysis of attachment
- Attackers use technology to create thousands of variants in seconds
- No sandbox, only checks against limited signature list of known threats stored on email device
No ability to decrypt and analyze
- Policy either automatically allows through or
- Automatically blocks resulting in business disruption
Designed to evade
- ShurL0ckr
- NoRelationship
- Cerber
Designed to specifically evade O365
Email Vulnerabilities
Email is the primary way that ransomware gets inside a business’s network. Many users still unintentionally open a malicious attachment or URL that slips by consumer-grade email filters. More often these days, attackers rely on social engineering and business email compromise (BEC) scams where users unknowingly give attackers the information they seek to set off a series of events—like getting the victim’s phone number and replicating known sites to obtain user credentials. For SMBs that often rely on consumer-based email solutions that lack advanced email security checks, recognizing threats and avoiding social engineering schemes rely on a user’s individual judgment to identify the threat and avoid infection.
How Malicious Emails Circumvent Security
Malicious URLs Embedded in Email
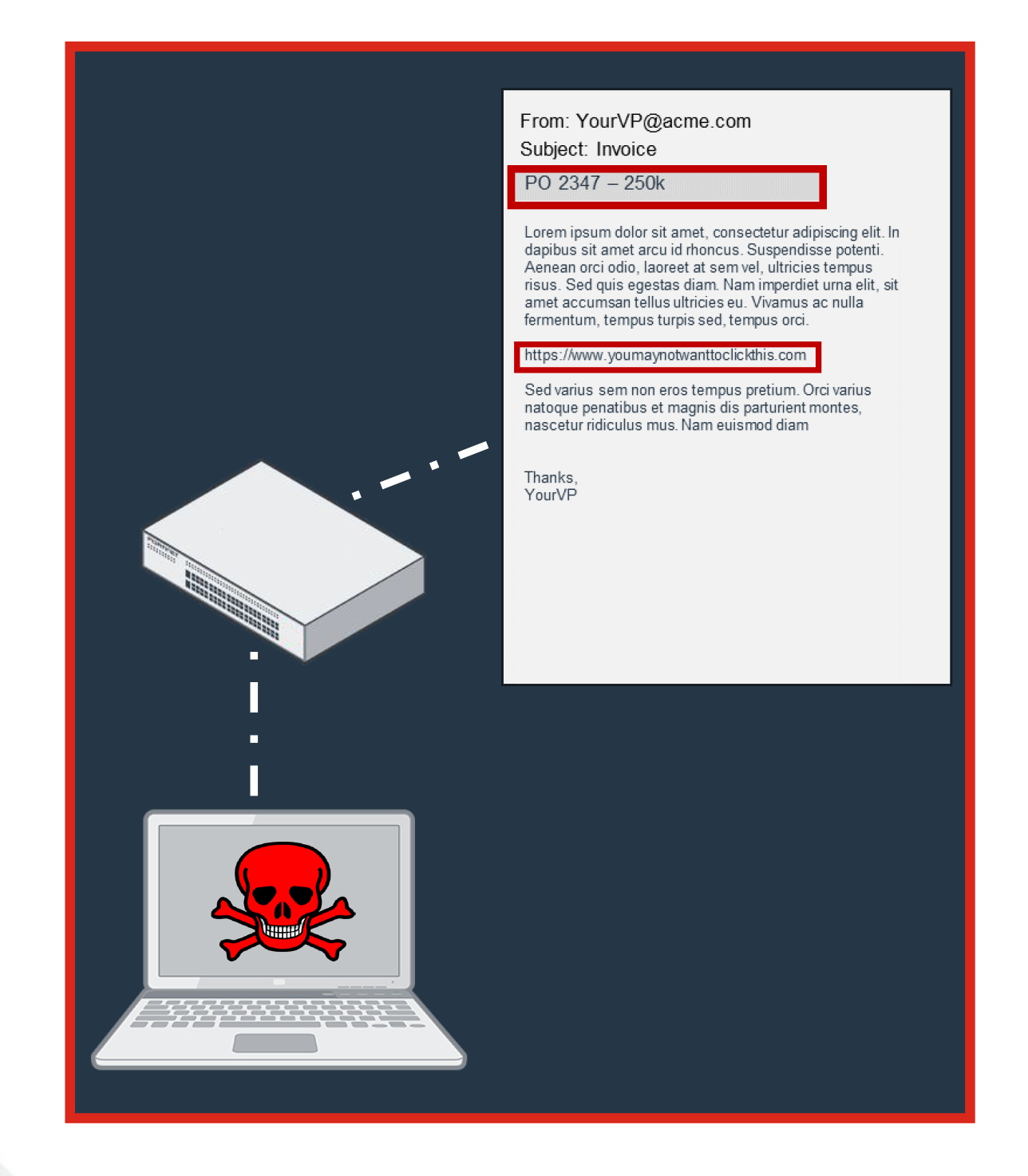
Inadequate analysis on target website
- Only checks against limited list of known malicious sites
- Infrequent updates and only included with premium version
Can't analyze embedded links
- Attachment text scanning isn't included
- If attachment is encrypted, can't decrypt and analyze
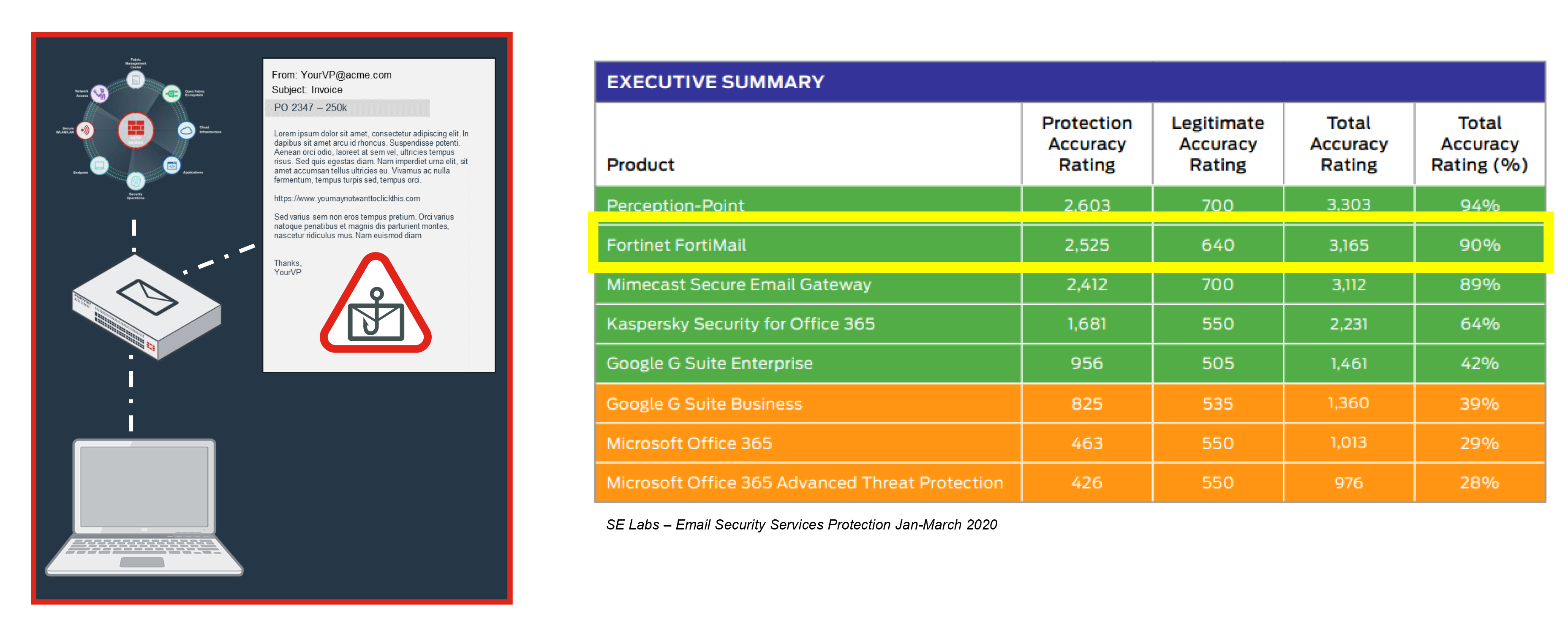
Fortinet Email Security
The FortiMail family of appliances is a proven, powerful messaging security platform for any size organization, from small businesses to carriers, service providers, and large enterprises. Purpose-built for the most demanding messaging systems, the FortiMail appliances utilize Fortinet's years of experience in protecting networks against spam, malware, and other message-borne threats.
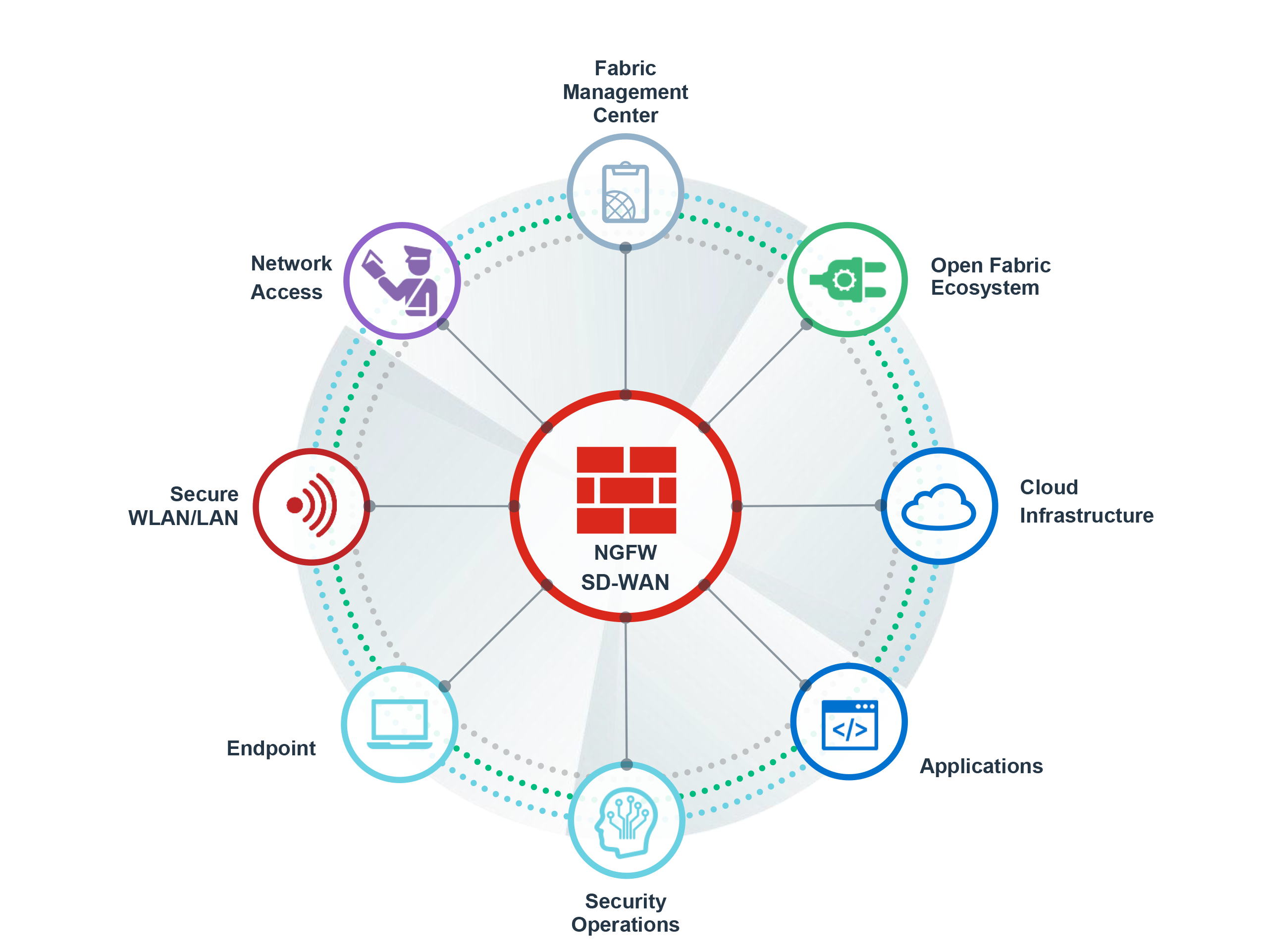
Fortinet Security Fabric
Broad
visibility of the entire digital attack surface to better manage risk
Integrated
solution that reduces the complexity of supporting multiple point products
Automated
workflows to increase speed of operations and response
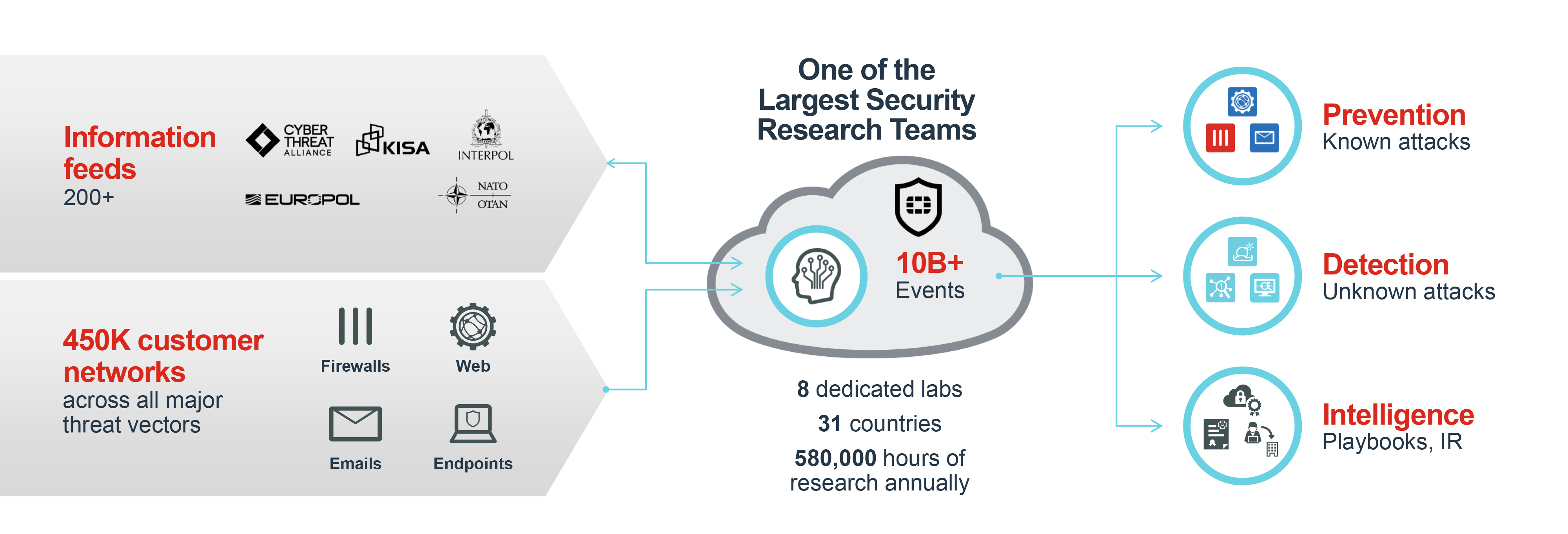
FortiGuard Labs AI-Driven Intelligence
Billions of events analyzed every day
How Fortinet Secures Email
Malicious Attachments

Advanced analysis of known and unknowns
- Identifies zero day and previously unknown malware through a combination of AI & ML
- Distributes threat intelligence across platform, updating “Known” malware lists for your environment and all customers
Decrypts and analyzes
- Text scanning for password to open and analyze
Content Disarm and Reconstruct
- Strips all active content from email and delivers text friendly, safew email with the ability to retrieve analyzed content
How Fortinet Secures Email
Malicious URLs Embedded in Email

Advanced threat analysis on target website
- Checks against known list of good and bad sides
- Click Protect: Real time website rescan before user travels
- Web filtering enables additional grouping of 87 categories to enhance basic policy controls
Analysis of embedded links
- Applies same check as if in body of email
- If encrypted, text scanning for password to open and analyze
How Fortinet Secures Email
Phishing
Common Network Security Limitations
How Malicious Sites Circumvent Security
Drive by Downloads
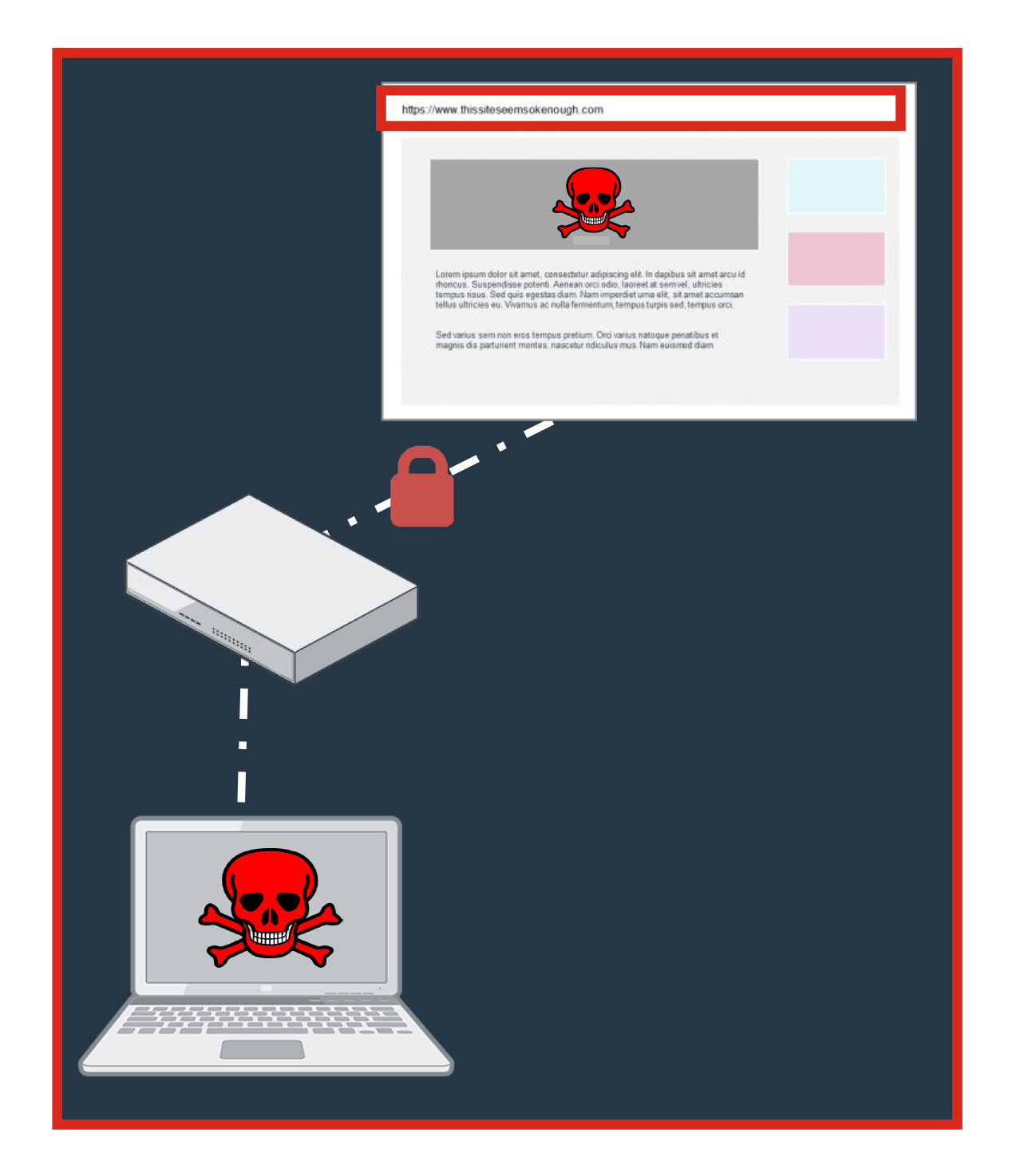
Limited policy controls to control browsing
- Only able to black and white list specific sites and key words
- Site has been weaponized since last scan deemed it safe
Inadequate analysis on incoming traffic
- Attackers use technology to create thousands of variants in seconds
- Only checks against limited signature list of known threats
- Data is encrypted and firewall can’t decrypt
No firewall in place or VPN unused
- As users travel to malicious sites, malware is downloaded
How Attackers Circumvent Network Security
Avoiding the Firewall
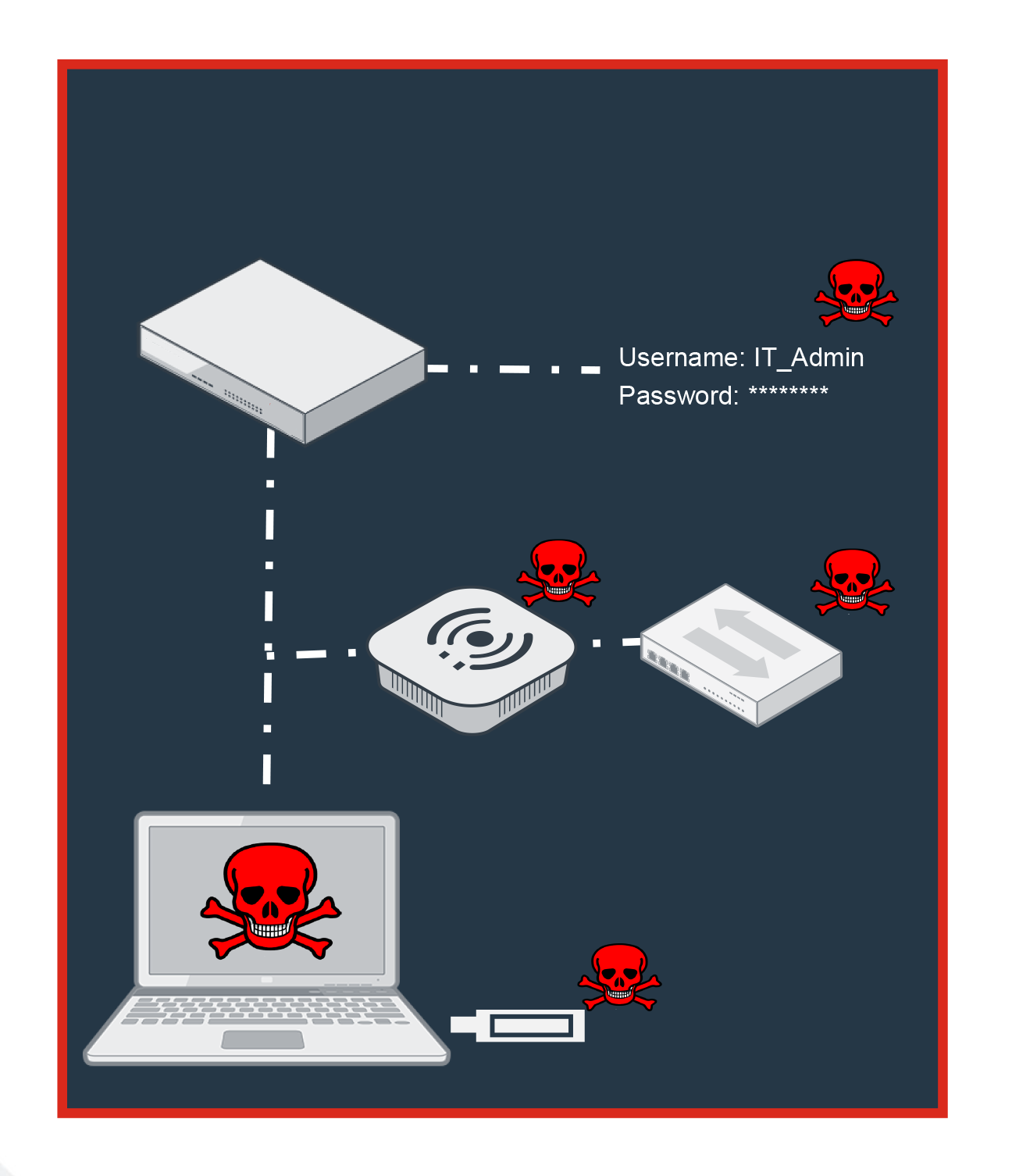
No threat analysis on traffic from wireless or wired devices
- Not connected to firewall with limited if any security
Inadequate analysis on attached devices
- No sandbox, only checks against limited signature list of known threats stored on endpoint agent
No multi-factor authentication to block stolen credentials
- Applications presume the stolen credentials are valid without an additional check to ensure it’s the true user
Fortinet Security Driven Networking
Fortinet AI Driven Security
How Malicious Sites Circumvent Security
Drive by Downloads
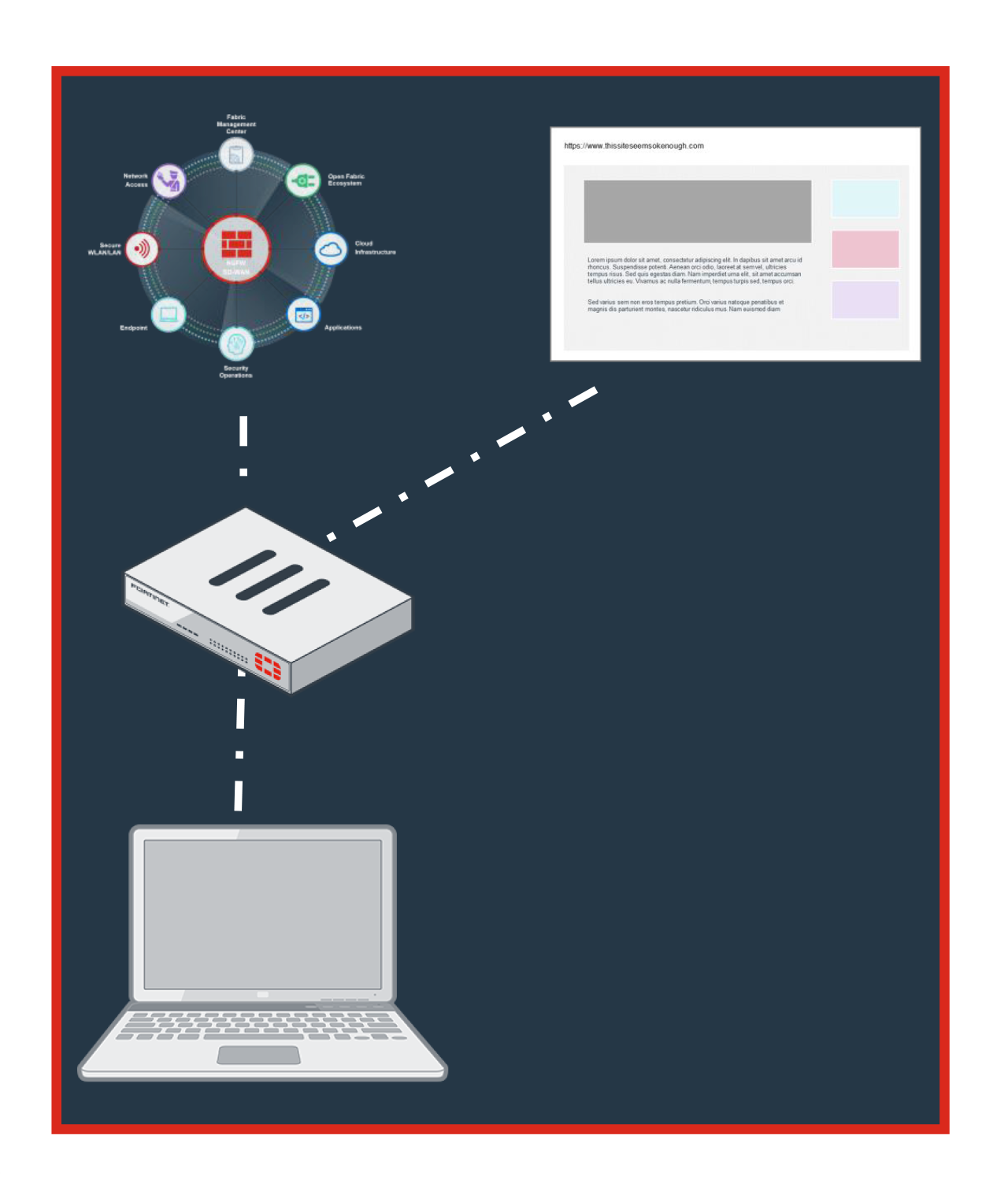
Enhanced policy controls to control browsing
- Checks against known list of good and bad sides
- Web filtering enables additional grouping of 87 categories to enhance basic policy controls
Advanced analysis of unknowns
- Identifies zero day and previously unknown malware through a combination of AI & ML
- Distributes threat intelligence across platform, updating “Known” malware lists for your environment and all customers
- Ability to decrypt incoming traffic without significant impact to throughput
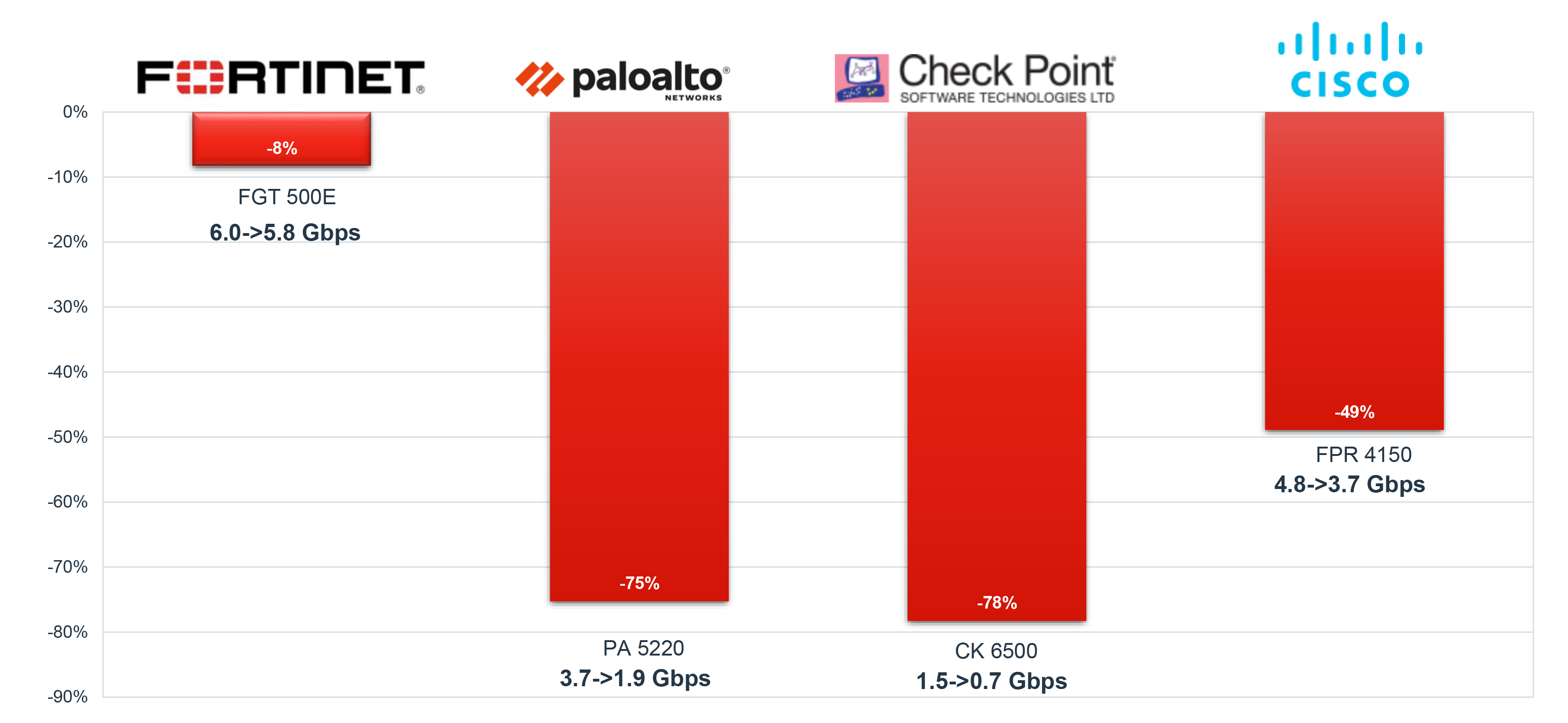
Fortinet Superior SSL Performance
NSS Labs NGFW 2019 New SSL Performance Test
Gartner’s 2019 Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls
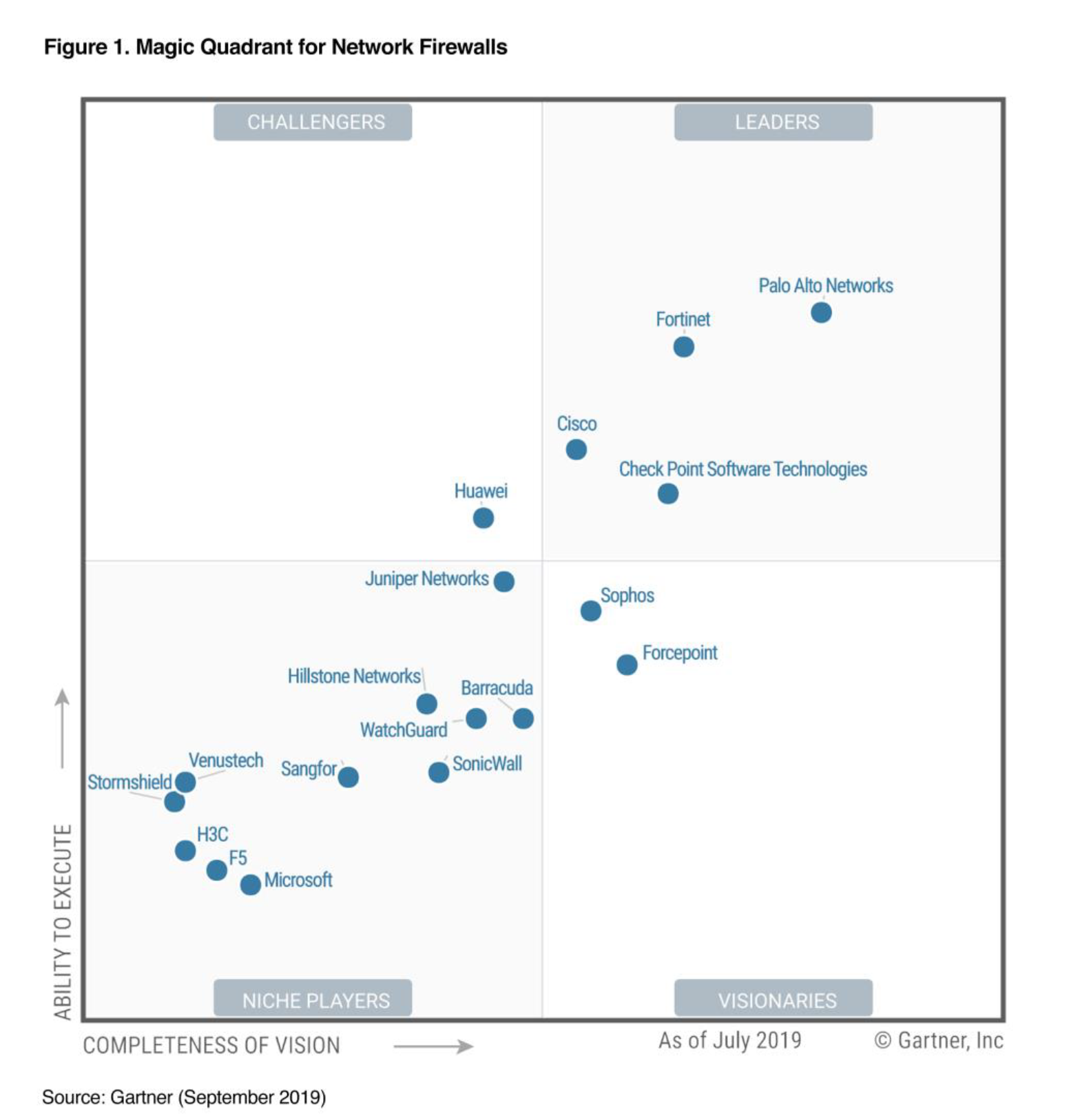
Fortinet Recognized as a Leader in this Magic Quadrant
Marks 10th time in a row that Fortinet is in the Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls
Gartner Magic Quadrant for Network Firewall, Rajpreet Kaur , Adam Hills,, Jeremy D’Hoinne , John Watts, 17, September 2019. This report was previously titled the Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Networks Firewalls.
This graphic was published by Gartner, Inc. as part of a larger research document and should be evaluated in the context of the entire document. The Gartner document is available upon request from Fortinet
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner's research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose
How the Fortinet Security Fabric Protects You
Avoiding the Firewall
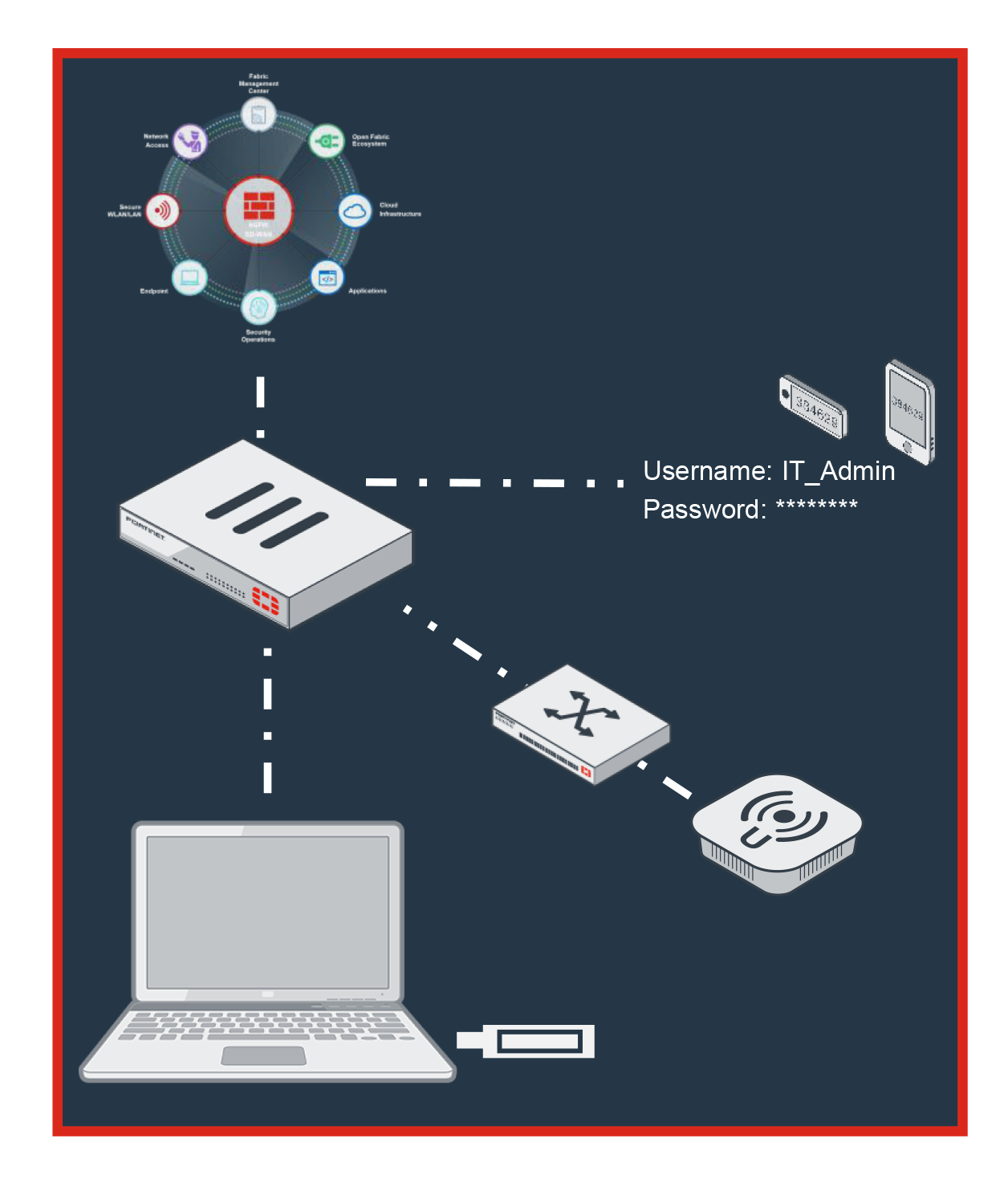
Security extended to wireless and wired devices
- Proprietary technology built into OS enables FortiAP and FortiSwitch to become extensions of the FortiGate NGFW
Advanced analysis of unknowns on endpoint
- Identifies zero day and previously unknown malware through a combination of AI & ML
- Distributes threat intelligence across platform, updating “Known” malware lists for your environment and all customers
Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
- FortiToken enables two factor authentication on mobile devices of physical token
Fortinet Protects Across Your Environment

NSS Labs 3rd Party Certifications
Most recent test results